Nuclear physics
What is nuclear
Ans : nuclear physics is the study of the structure of
nuclei their formation stability and decay
Properties of nucleus
- Nuclear size
- Nuclear mass
- Nuclear density
- Nuclear charge
- Nuclear spin
Nuclear size :
V ∝ A (where V = volume of
sphere , A = atomic mass number )
Nuclear mass :
M = Zmp + ( A – Z )mn
[where Z = Atomic number or number of proton
mp = Rest
mass proton
A – Z =
Number of nutron
mn =
Rest mass of nutron ]
mass
spectrograph is the device which is use to measure the mass of nucleus
Nuclear density :
Nuclear
charge :
Nucleus charge q = +Ze
Z = atomic number
e = charge of proton
nuclear
spin :
Nuclear magneton
is the unit to measure nuclear spin
e = charge of proton
h = planks constant = 6.625×10-34
nuclear forces :
the forces which binds the nucleons together inside the nucleus are called nuclear forces. Protons and neutrons are commonly called nucleons. in between protons electrostatic force of repulsion is produced but inside the nucleus they have force of attraction hence nuclear forces have some special characters or properties
Properties or characteristics
1. Nuclear forces are attractive in nature
They do not have force of repulsion
2. They are strongest forces
Nuclear force between nucleons is 100 times stronger than the electromagnetic force and 1038 times stronger than the gravitational force.
3. They are charge independent forces
The strength of the nuclear forces between pair of protons is equal to force between pair of neutrons which is equal to force between proton and neutron
∴ 𝐹𝑝𝑝 = 𝐹𝑛𝑛 = 𝐹𝑝𝑛
4. They are non gravitational forces
Nuclear force between nucleus does not depend on gravity
5. They are non central forces
force between the nucleons does that act along the line joining the centre of nucleons
6. They are spin dependent forces
force between nucleons are stronger when the nucleons have like spin and they are weak when the nucleons have unlike spin
7. They have property of saturation
that is each nucleon interact with it’s immediate neighbours only, rather than with all other nucleons in the nucleus
8. Nuclear forces are short range forces
nucleons exert forces within the nucleus of range femto meter ( fm or 10-15 )
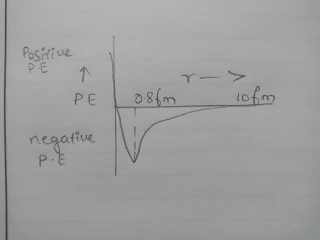
from the above graph
a. Nuclear forces are negligible when the distance between the nucleons is more than 10 fm
b. When the nucleons are brought closer, nuclear force of attraction develops which goes on increasing rapidly with the decreasing distance, however nuclear forces do not obey inverse square law
c. When the distance between nucleons becomes less than 0.8 femtometer the nuclear forces become strongly repulsive
From the above graph potential energy between pair nucleons is minimum at a distance 0.8 femtometer, at this distance force between nucleons is zero for distance larger than 0.8 femtometer, negative potential energy goes on decreasing the nuclear forces are attractive for adistance less than 0.8 femtometer negative potential energy decreases to zero and then becomes positive.
9. They are exchange forces
Force between the nucleons exchanges due to conversion of proton into neutron and neutron into proton by the emission or absorption of meson
Meson theory of nuclear forces
A Japanese physicist ‘yukawa’ postulated in the year 1936 that nuclear forces between the nucleus arise an account of continues exchange of particles called mesons, between the nucleons the nuclear forces of exchange by converting proton into neutron or neutron into proton by the absorption or emission of meson, later on these mesons were detected experimentally they were found to have a mass about 270 times the mass of an electron they’re
three type of mesons,
• Neutral pi (π) meson carries no charge
• Positive pi (π) meson carries unit positive charge
• Negative pi (π) meson carries unit negative charge
Liquid drop model
In the liquid drop model, the forces acting in the nucleus are assumed to be analogical to the molecular forces in a droplet of some liquid, this model was proposed by Neils bohr. the similarities between the nucleus and the liquid drop are the following
1. The liquid drop is spherical in shape similarly stable nucleus is also in spherical shape.
2. The force of surface tension acts on the surface of liquid drop, similarly there is a potential barrier at the surface of nucleus.
3. The density of a liquid drop is independent of its volume similarly the density of the nucleus is independent of its volume.
4. The intermolecular forces in a liquid are sharp range forces similarly nuclear forces are sharp range forces.
5. The molecules in a liquid drop interact only with their immediate neighbours, similarly nucleons in the nucleus also interact only with their immediate neighbours this leads to the saturation in a nuclear forces and a constant binding energy per nucleon.
6. The molecules evaporate from a liquid drop on raising the temperature of the liquid due to their increased thermal energy similarly when the energy is given to a nucleus by bombarding it with nuclear projectiles a compound nuclear is formed which emits the nuclear radiations.
7. When a small drop of liquid is allowed to oscillate, it breaks up into two smaller drops of equal size, the process of nuclear fission is similar and the nucleus breaks up into two smaller nuclei.
semi empirical mass formula :
the liquid drop model can be used to obtain an expression for the binding energy of nucleus. weizacker proposed the semi empirical nuclear binding energy formula for a nucleus of mass number A, containing Z protons and N neutrons it is given by
this is called semi empirical mass formula where a, b, c, d and 𝛿 are constants.
Click here to download Nuclear physics Pdf
Continued topic uploading Soon 🔜..........



















0 Comments